This content has been automatically translated from Ukrainian.
Bubble Sort is one of the simplest sorting algorithms. Its essence lies in comparing adjacent elements of the array and swapping them if they are in the wrong order. Thus, the "heaviest" element gradually "bubbles" to the end of the array, like a bubble in water, hence the name of the algorithm.
How it works in simple terms:
- Take an array of numbers
- Compare the first number with the second
- If the first is greater than the second - swap them
- Move to the next pair and repeat
- Repeat the whole process several times until the array is sorted
Example implementation in Ruby:
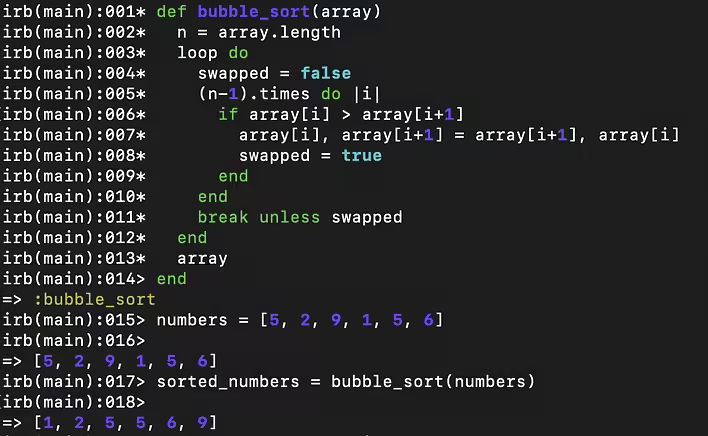
def bubble_sort(array)
n = array.length
loop do
swapped = false
(n-1).times do |i|
if array[i] > array[i+1]
array[i], array[i+1] = array[i+1], array[i]
swapped = true
end
end
break unless swapped
end
array
end
numbers = [5, 2, 9, 1, 5, 6]
sorted_numbers = bubble_sort(numbers)
Type something like this in the terminal:
- swapped tracks whether there were changes in the current pass
- If there were no changes in one pass - the array is sorted and we can stop
- array[i], array[i+1] = array[i+1], array[i] swaps two elements
Bubble Sort is easy to understand, but it is slow for large arrays, so faster sorting algorithms are often used for practical tasks.
This post doesn't have any additions from the author yet.