Table of contentsClick link to navigate to the desired location
This content has been automatically translated from Ukrainian.
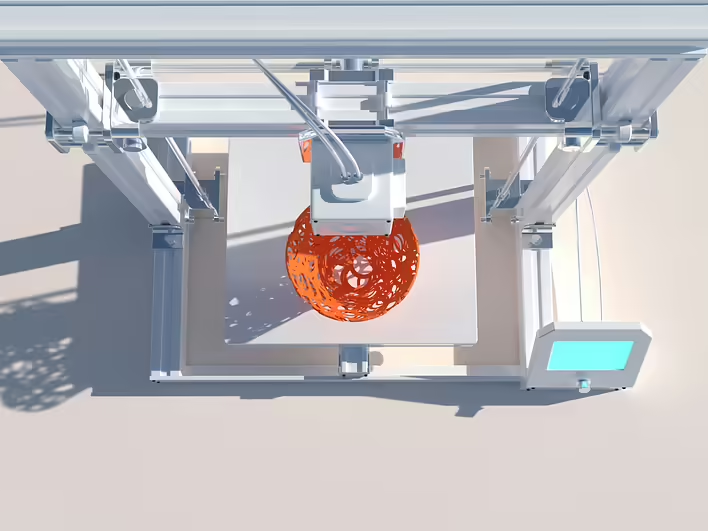
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) (sometimes Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF)) is a common method of 3D printing that is based on the layer-by-layer deposition of melted thermoplastic material to create three-dimensional objects.
The process begins with feeding a plastic filament (filament) into a heated extrusion head, where the material melts. The melted plastic is extruded through a nozzle and deposited onto a platform layer by layer according to a digital model. Each layer hardens upon cooling, bonding with the previous one, allowing the object to be gradually formed.
The FDM technology was developed in the late 1980s by Scott Crump, co-founder of Stratasys, and commercially implemented in the early 1990s. After the patent for this technology expired in 2009, it became widely available for use, contributing to the rise in popularity of 3D printing among enthusiasts and small businesses.
Materials and Applications of FDM Printing
FDM printers can work with various thermoplastic materials, such as:
- PLA (polylactic acid)
- ABS (acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene)
- PETG (polyethylene terephthalate glycol)
- TPU (thermoplastic polyurethane)
These materials have different mechanical properties and temperature characteristics, allowing for the selection of the optimal option for specific tasks. FDM printing is widely used for prototyping, manufacturing functional parts, educational purposes, and in many other fields.
Advantages include:
- Affordability and relatively low cost of equipment and materials.
- Ease of use and maintenance.
- The ability to quickly produce prototypes and small batches of products.
Nuances:
- Visibility of layers on the surface of the product, which may require additional finishing (sanding; can be physical or chemical).
- Limited accuracy and detail compared to other 3D printing methods, such as stereolithography (SLA).
- Not all materials are suitable for FDM printing due to requirements for melting temperature and adhesion between layers.
FDM is a very common type of printing, but when choosing a printer, one should consider 3D printing technologies for specific tasks.
This post doesn't have any additions from the author yet.