Table of contentsClick link to navigate to the desired location
This content has been automatically translated from Ukrainian.
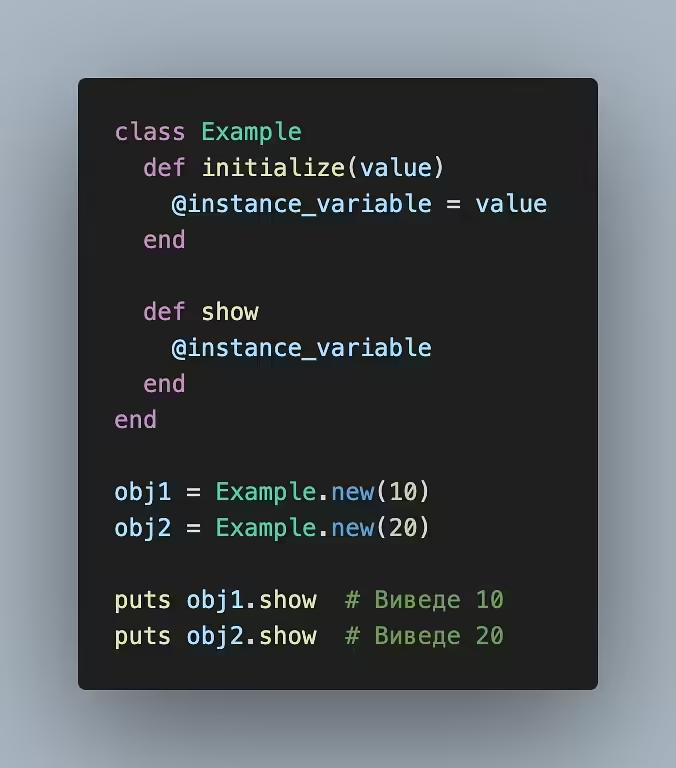
A function is the fundamental building block of programming that defines a set of instructions or actions that are executed when it is called. Functions allow you to organize code into understandable and reusable blocks. Functions can take input data (arguments) and return a result.
In different programming languages, functions may have different names, such as "methods" in object-oriented programming. The term method is more commonly heard in discussions about Ruby code, while the term function is used for JS.
Characteristics of Functions
- A function has a name by which it can be called.
- A function can take one or more arguments – input data used to perform calculations or actions within the function.
- It is a set of instructions that are executed when the function is called.
- A function can return a value as a result of its execution.
Conceptually, this is a list of the main characteristics that functions have. Let's look at examples (Ruby and JS)
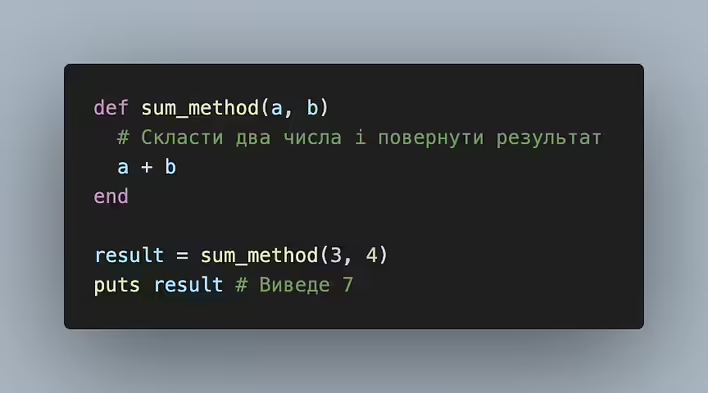
Example of a Function (Method) in Ruby
def sum_method(a, b) # Add two numbers and return the result a + b end result = sum_method(3, 4) puts result # Will output 7
Example of a Function in JavaScript
function sumFunction(a, b) {
// Add two numbers and return the result
return a + b;
}
let result = sumFunction(3, 4);
console.log(result); // Will output 7
What are Functions for?
Functions allow you to reuse code and avoid duplication. For example, if you need to perform the same calculations in different places in the program, you can define a function and call it whenever needed. Functions are the foundation ^_^
This post doesn't have any additions from the author yet.




![[Fix] extconf.rb failed during the installation of the Ruby library Gosu](https://d3kb0xa9zqcv9v.cloudfront.net/ph1rtiabxj2jh76ht1pjn1in80n2)