Table of contentsClick link to navigate to the desired location
This content has been automatically translated from Ukrainian.
In Ruby, there is only one type of integer — Integer. In previous versions of Ruby, there were separate classes for integers of different sizes, such as Fixnum for small integers and Bignum for large integers. Starting from Ruby version 2.4, these classes were merged into a single class Integer.
In Ruby, there is no distinction between int and bigint, as in databases. The single Integer class can represent both small and large integers. This feature allows Ruby to work seamlessly with any integers, regardless of their size.
13.class => Integer 9223372036854775808.class => Integer
However, in the context of databases such as PostgreSQL, we often encounter data types int and bigint, which represent 32-bit and 64-bit integers respectively. In Ruby, we can work with either of these data types, but it is important to understand how they differ in the database and how Ruby handles large numbers.
Difference between int and bigint
To simplify - bigint can hold a larger maximum integer. That is, if you try to push a number too large into int - you will get an error. For this, we need a data type that can accept larger values. This is useful in the context of large databases. If you know the database will be large - use bigint. Otherwise, at some point, you will have to write migrations from int to bigint (technical debt will accumulate, which can be avoided by knowing the approximate/potential scale of the database).
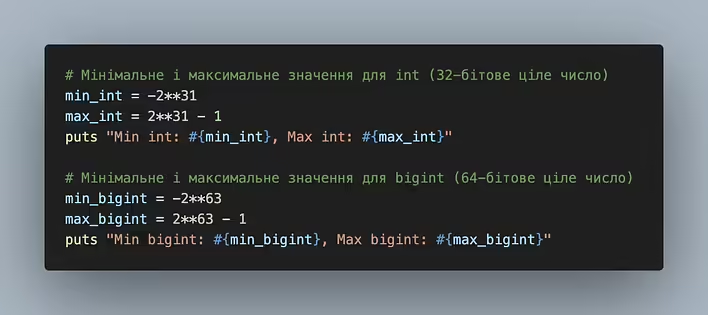
Minimum and maximum values for int and bigint
Okay. Let's calculate the maximum numbers that int and bigint can have:
# Minimum and maximum value for int (32-bit integer)
min_int = -2**31
max_int = 2**31 - 1
puts "Min int: #{min_int}, Max int: #{max_int}"
Min int: -2147483648, Max int: 2147483647
# Minimum and maximum value for bigint (64-bit integer)
min_bigint = -2**63
max_bigint = 2**63 - 1
puts "Min bigint: #{min_bigint}, Max bigint: #{max_bigint}"
Min bigint: -9223372036854775808, Max bigint: 9223372036854775807
If you add a number beyond these ranges - you will get an SQL error:
ERROR: integer out of range # for int ERROR: bigint out of range # for bigint
If you try to save a value through a Rails app - you will see ActiveRecord error.
This post doesn't have any additions from the author yet.





![[Fix] extconf.rb failed during the installation of the Ruby library Gosu](https://d3kb0xa9zqcv9v.cloudfront.net/ph1rtiabxj2jh76ht1pjn1in80n2)