Table of contentsClick link to navigate to the desired location
This content has been automatically translated from Ukrainian.
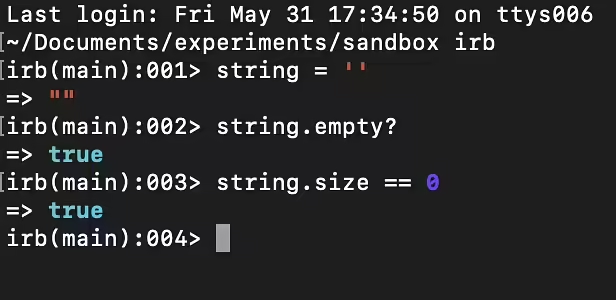
In Ruby, both nil and false are used to represent the concept of "nothing" or "falseness," but they have different roles and behaviors. Understanding the differences between them is important for writing clear and effective Ruby code.
Characteristics of the nil value
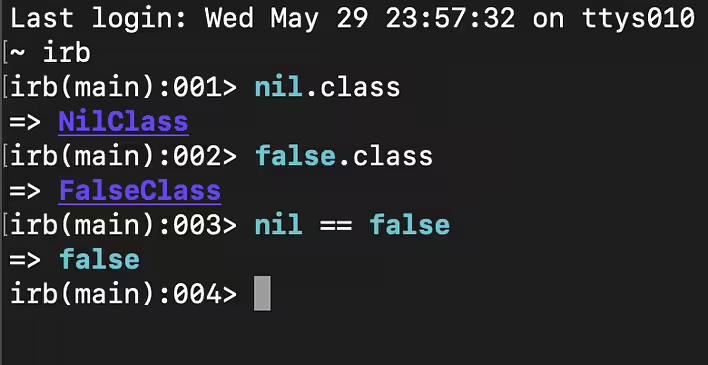
- Type: nil is an instance of the NilClass.
- Value: Represents the absence of a value or "nothing." It is often used to indicate that a variable has not been assigned any value or that a method has not returned any result.
- Truthiness: nil is considered "false" in conditional expressions. This means that in an if statement, nil will be treated as a false value.
For example:
value = nil if value puts "This code will not be executed" else puts "The value variable is nil" end
Result:
The value variable is nil => nil
Characteristics of the false value
Type: false is an instance of the FalseClass.
Value: Represents a logical false value. Used in logical operations to indicate that a condition is false.
Truthiness: false is considered "false" in conditional expressions. This means that in an if statement, false will be treated as a false value.For example:
value = false if value puts "This code will not be executed" else puts "The value variable is false" end
Result:
The value variable is false => nil
Why do we see nil after the printed text? Read in the post - Why does Ruby code return nil after executing puts?
The main difference between nil and false lies in their meaning and usage. nil means the absence of a value or "nothing," while false means logical falseness. Both values are considered false in conditional expressions, but their meaning and usage differ. This allows distinguishing situations where a variable has no value (nil) and where a condition is logically false (false).
That is, nil is used to describe emptiness. False is used to denote falseness.
- If we need to return a false result for validation is_valid?, we should return false.
- If we need to clear a value - we use nil.
- And in a conditional expression, both nil and false yield a false result.
Let's check:
def check_value(value)
if value
puts "The value is true"
else
puts "The value is false (nil or false)" # This will be output for nil and false
end
end
check_value(nil) # Outputs: The value is false (nil or false)
check_value(false) # Outputs: The value is false (nil or false)
check_value(true) # Outputs: The value is true
check_value(1) # Outputs: The value is true
check_value("Hello")# Outputs: The value is true
In the characteristics of values, we mentioned NilClass and FalseClass. Personally, I have never seen these classes touched when working with Ruby, but let's consider them for purely academic purposes.
FalseClass
FalseClass is a built-in class in Ruby that represents logical falseness. In Ruby, only two values are considered false in conditional expressions: false and nil. Here are a few key points:
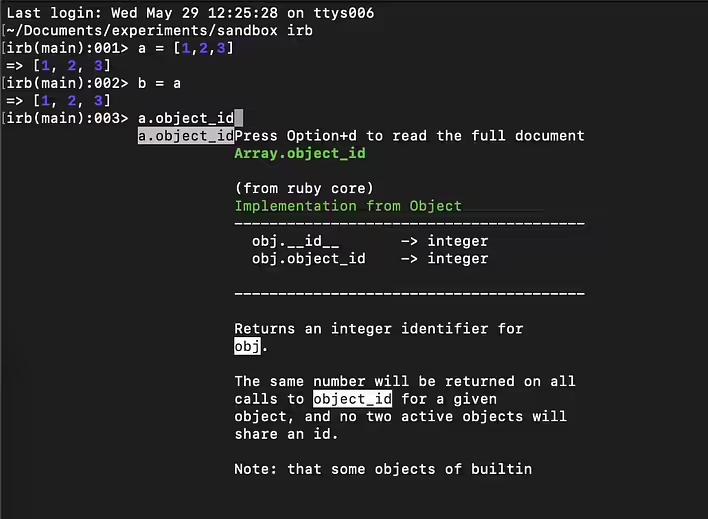
- In Ruby, false is the only instance of the FalseClass. This means that all variables that have the value false refer to the same object. More details about immediate values have already been written here.
- The value false is often used in logical operations and conditional expressions to indicate a false condition.
- The FalseClass has several methods, among which the most common are &, |, and ^ for performing logical operations.
is_valid = false puts is_valid.class # => FalseClass # Using in a conditional expression if is_valid puts "This code will not be executed" else puts "is_valid is false" # This will be output end # Logical operations puts false & true # => false puts false | true # => true puts false ^ true # => true
So FalseClass holds the value false and also has methods for performing logical operations.
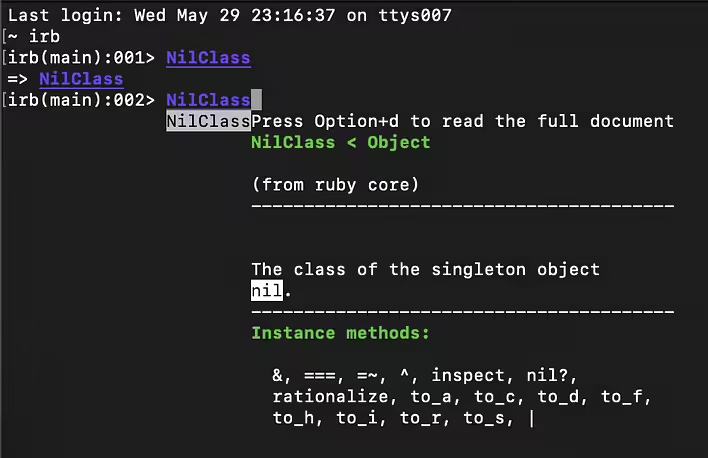
NilClass
NilClass is also a built-in class in Ruby that represents the absence of a value or "nothing."
- In Ruby, nil is the only instance of the NilClass. This means that all variables that have the value nil refer to the same object.
- The value nil is often used to indicate the absence of a value or an undefined state.
- The NilClass has several methods, including nil?, which always returns true for the nil object, as well as methods for converting to other types (to_s, to_i, to_f).
NilClass Instance methods: &, ===, =~, ^, inspect, nil?, rationalize, to_a, to_c, to_d, to_f, to_h, to_i, to_r, to_s, |
An example of interaction with NilClass
value = nil puts value.class # => NilClass # Using in a conditional expression if value puts "This code will not be executed" else puts "value is nil" # This will be output end # NilClass methods puts nil.nil? # => true puts nil.to_s # => "" puts nil.to_i # => 0 puts nil.to_f # => 0.0
NilClass is needed to work with the nil value (similarly to FalseClass).
This post doesn't have any additions from the author yet.