This content has been automatically translated from Ukrainian.
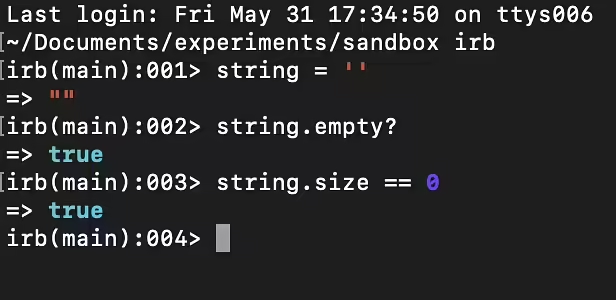
In Ruby, the puts method always returns nil after printing a string to the screen. This is standard behavior for puts, as its main purpose is to output text rather than return a value. In other words, puts is an output method, and its side effect (outputting text) is more important than the returned value.
result = puts "Hello, world!" Hello, world! => nil
When you execute the code "puts 'Hello, world!'", irb will print "Hello, world!" to the screen and return nil. Thus, the variable result will have the value nil.
result => nil
Why does this happen?
The puts method is designed to output data to the standard output stream (usually, the console). Returning a value is not its primary function. Therefore, for convenience and consistency, puts always returns nil. This is simply something to remember.
Many methods in Ruby that have side effects (such as outputting to the screen or modifying an object) return nil or the object on which they are called. This makes their behavior predictable and allows for easy understanding that the main action of the method occurred as a side effect, rather than through the returned value.
An example with a method:
def say_hello puts "Hello!" end result = say_hello result => nil
The same rule applies to conditional expressions. In Ruby, every expression returns a value. When you execute code that contains conditional operators or methods, Ruby always returns the result of the last executed expression. In the following example, you get => nil because the last expression in the code is the if conditional operator, which returns the value of the last executed block.
value = false if value puts "This code will not be executed" else puts "The variable value is false" end Result: The variable value is false => nil
Let's break it down in detail.
value = false if value puts "This code will not be executed" else puts "The variable value is false" end
In this code, the variable value is false. The if operator checks the value of value. Since value is false, Ruby executes the block of code inside else.
puts "The variable value is false"
The puts method outputs the string "The variable value is false" and returns nil, because puts always returns nil after printing a string to the screen. Thus, the result of executing the else block is nil.
As a result, when the if conditional operator finishes execution, it returns the value of the last executed expression, which is the result of puts, that is, nil.
Therefore, you see:
The variable value is false => nil
I hope this question is clear now ^_^
This post doesn't have any additions from the author yet.