Table of contentsClick link to navigate to the desired location
This content has been automatically translated from Ukrainian.
An empty string in Ruby is not false. Programmers like to compare this nuance with Perl, because in Perl an empty string is false.
It should be remembered that in Ruby the false values are only nil and false.
In Ruby, conditional expressions are evaluated based on the truthiness or falsiness of values. Of all possible values in Ruby, only two are false: nil and false. All other values, including an empty string (""), are considered true.
This means that when using an empty string in a conditional expression, it will always be treated as true. To check if a string is empty, several approaches can be used:
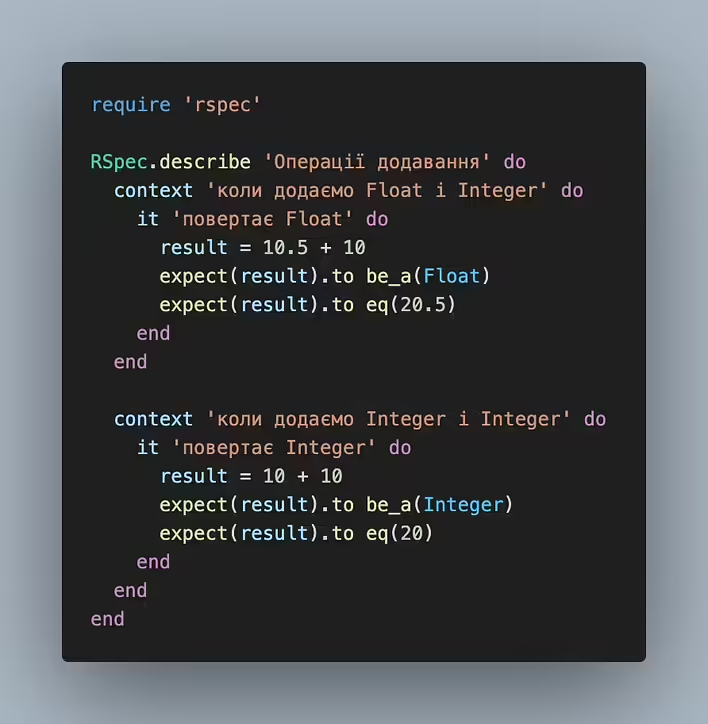
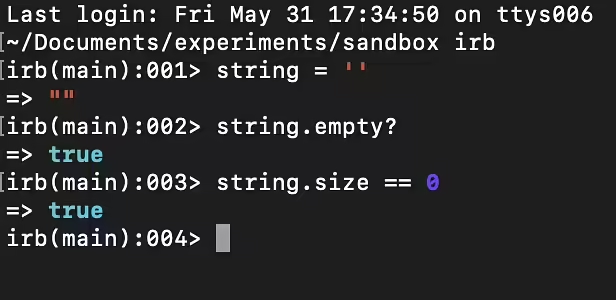
Method empty?
str = "" puts "Empty string" if str.empty? Empty string => nil
We see that str.empty? returned true and printed the response. Next, we see nil, but why - read more in this post.
Ruby has built-in methods that allow you to show whether a string is empty. And these methods should be used in conditional expressions to make the code as clear as possible.
Comparison with an empty string
str = ""puts "Empty string" if str == ""Empty string=> nil
Ruby is a cool language and allows you to do the same things in different ways. So if desired, you can use comparisons with an empty string in conditional expressions.
Checking the length of the string
str = "" puts "Empty string" if str.size == 0 # or puts "Empty string" if str.length == 0
As I wrote - ruby allows you to do the same things in different ways (note the size and length methods).
Why does an empty string return true?
It may seem illogical because '' is something that resembles nothing / emptiness. But let's delve into this a bit.
In Ruby, it is easier to consider all objects, except nil and false, as true. This reduces the number of special cases that a programmer needs to remember. Ruby is built on the principle that everything is an object. This means that every value, including an empty string, must be an object and have certain behavior. Since an empty string is an object of the String class, it is considered true. By considering an empty string as true, Ruby simplifies conditional expressions and makes the code more predictable. For example, in conditional expressions, you can always rely on the fact that only nil and false will be considered false.
str = "" if str puts "String is not nil or false" else puts "String is nil or false" end
By the way, let's prove that an object of the String class (namely an empty string) is not an immediate value. An empty string (like any object of the String class) is not an immediate value, but is represented as an object in memory. In Ruby, only nil and false are false in conditional expressions. All other values, including an empty string, are considered true (truthy).
str1 = "" str2 = "" puts str1.object_id == str2.object_id => false # That is, each string has its own object_id str1.object_id => 46820 str2.object_id => 46800
So we have two different String objects with empty content. And the object returns true in conditional expressions.
This post doesn't have any additions from the author yet.