Table of contentsClick link to navigate to the desired location
This content has been automatically translated from Ukrainian.
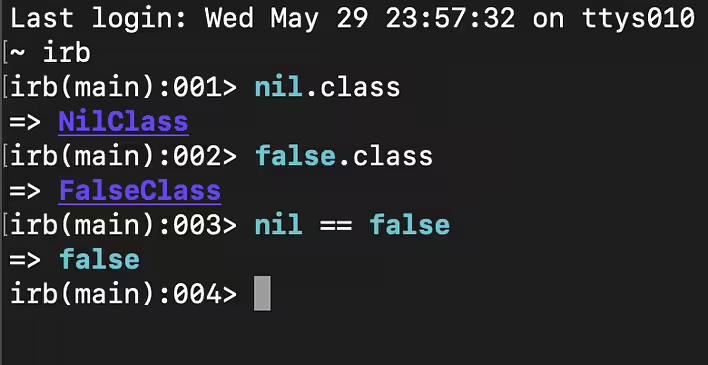
Immutability and mutability are properties of objects (in programming and other fields) that determine whether objects can change after their creation. I looked up how to correctly spell it - mutabLE or mutabILity, and it seems that both options are correct (but I'm not sure ^_^).
Example of Immutability
Imagine a photograph that you took and printed. Once the photograph is printed, you cannot change its content. If you don't like that someone in the photograph has their eyes closed, you cannot change that photograph – instead, you will have to take a new one. In this example, the photograph is immutable.
Example of Mutability
Now imagine a clay figure that you are sculpting. If you decide that you want to change the shape of the nose on the figure, you can easily do so by reshaping the clay. In this example, the clay figure is mutable.
Example from Programming (Ruby)
Strings in many programming languages are immutable. This means that once a string is created, its value cannot be changed. However, each language has its nuances, and depending on the version of the language, the concept of immutability/mutability may vary.
For example, in Ruby - String can mutate. Let's check (ruby 3.2.1):
str = "Hello" puts str.object_id => 1960 str.upcase! => "HELLO" puts str => HELLO puts str.object_id => 1960
That is, using the upcase! method, we changed the text of the variable.
If we want strings to remain unchanged, we need to add a magic comment at the beginning of the Ruby script:
# frozen_string_literal: true
So, our file (example.rb) will look like this:
# frozen_string_literal: true str = "Hello" puts str.object_id str.upcase! puts str puts str.object_id
And the result of running it will be as follows:
ruby ~/Desktop/example.rb 60 /Users/user/Desktop/example.rb:5:in `upcase!': can't modify frozen String: "Hello" (FrozenError) from /Users/user/Desktop/example.rb:5:in `<main>'
We see that the script printed - 60. This is the result of the code puts str.object_id. Then we get a runtime error trying to modify the String - can't modify frozen String: "Hello" (FrozenError). This means we enabled freezing of values (string literal) and now we get an error when trying to modify. It is said that Ruby 3.4 will have frozen literals by default. So we will need to add the option --disable-frozen-string-literal or something similar to avoid errors after the update. Let's see.
Immutability and mutability are fundamental concepts in programming that help programmers manage the state of objects and their changes. Using immutable objects can make code more predictable and easier to test, while mutable objects can be more convenient for modeling dynamic systems.
This post doesn't have any additions from the author yet.




![[Fix] extconf.rb failed during the installation of the Ruby library Gosu](https://d3kb0xa9zqcv9v.cloudfront.net/ph1rtiabxj2jh76ht1pjn1in80n2)