Table of contentsClick link to navigate to the desired location
The model of intersectoral material connections is used in short- and medium-term forecasting for various calculations of balanced economic development of the country (region).Main quadrants of the modelGeneral scheme of the value creation chain (example for material production)Main concepts and terms
This content has been automatically translated from Ukrainian.
The model of intersectoral material connections is used in short- and medium-term forecasting for various calculations of balanced economic development of the country (region).
Three typical tasks can be identified:
- determining production volumes by sectors that provide the specified options for final consumption
- determining final consumption volumes based on the specified production volumes of sectors
- calculating production volumes and final consumption with a mixed composition of unknowns
Main quadrants of the model
First quadrant — distribution of products among sectors (intermediate products)
Second quadrant — final products of all sectors that move from the production sphere to final use (for consumption and accumulation)
Third quadrant — value structure of gross domestic product and imports (wages, taxes, subsidies, net profit, etc.)
General scheme of the value creation chain (example for material production)
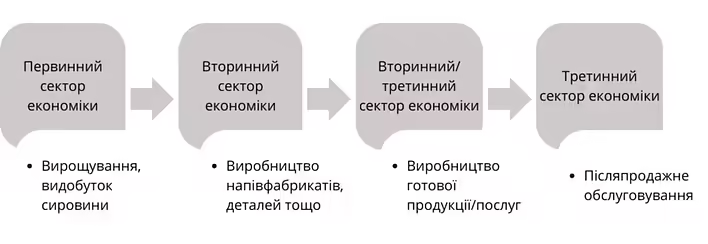
Main concepts and terms
Profitability (R) of the economies of the regions is defined as the percentage ratio of the net profit of enterprises in the territory (P) to the sum of its expenditures (S).
R=P/S*100 %
The economic efficiency of production is closely related to the indicator of labor productivity of the economy, which is based on the ratio of the volumes of produced (realized) products to labor costs. Labor productivity is measured by the amount of products or services produced by a worker per unit of time:
LP=V/L
where
LP — labor productivity
V — volumes of realized products (goods, works, services)
L — number of employees
Capital intensity or equipment intensity is the volume of fixed assets of the enterprise in monetary terms, which falls on one employee
Fₐ=F/L
where
Fₐ — capital intensity of labor
F — average annual balance value of active fixed assets
L — average annual number of employees (industrial production personnel)
Return on assets expresses the production relations regarding the economic efficiency of using production assets. The quantitative expression of return on assets is reduced to the ratio of the volumes of realized products (goods, works, services) to the volume of production assets used to obtain them:
Fᵣ=V/F
where
Fᵣ — return on production assets
V — volumes of realized products (goods, works, services) over a certain period of time
F — value of fixed assets used to obtain products over a certain period of time
Competitiveness of the enterprise is a comprehensive comparative characteristic of the enterprise that reflects the degree of advantage of the set of indicators of its activities that determine the success of the enterprise in a specific market over a specific period of time relative to the set of indicators of competitors
Competitiveness of the industry is determined by the presence of technical, economic, and organizational conditions for creating, producing, and selling high-quality products that meet the requirements of specific consumer groups
Competitive industry has a tendency to remain in a state of sustainable growth for a longer time
Competitiveness of the region is its ability, in conditions of competition based on the effective use of resources, to stimulate an increase in production productivity and the standard of living of the local population and, accordingly, to ensure a high competitive status in the geopolitical space in the long term
- Regions find themselves in a state not only of competitive struggle for promotion to external markets but also of struggle for their own markets and territory, which attract companies from other regions of the world
This post doesn't have any additions from the author yet.